Gitlab to Github Mirrors (PUSH)
5 min read
Oct 14, 2025

Woman in mirror by ChatGPT
What are mirrors?
In the simplest terms, mirrors are a way to get a copy of a repository onto another source control platform. There are two types of mirroring strategies: PUSH and PULL. This article will focus on the PUSH strategy on Gitlab.
The PUSH strategy means that when I push to my Gitlab repo the changes will eventually be mirrored (copied) to the corresponding Github repo.
Why am I writing this?
I'm writing because of two reasons. One, it's important to document certain processes. You don't have to do this process too often, so enough time passes in between time from one to the next that's enough to forget and cost you a couple of hours fumbling through it.
This doc is similar in quality to the tech docs that I've written on past jobs. They always came in handy as I moved from one engineering team to another while performing DevOps and MLOps duties.
Why do you need a mirror?
I can only answer this question for myself. Gitlab is free, extensible, and easy to use. Many other tools are capable of doing the job, but for this web app, I simply prefer Gitlab.
Another reason is that many of my other repos are in Github and I'm using Gitlab only for the CICD in this one repos. So when I direct people to my Github this repo will be represented along with all the others, even though it is actively contributed to on the Gitlab platform.
The Setup
First, I'm going to assume that you already have a Gitlab repository and a Github repository that you will be mirroring to.
Go to the destination repo on Github. Copy the SSH remote URL. See the image below.
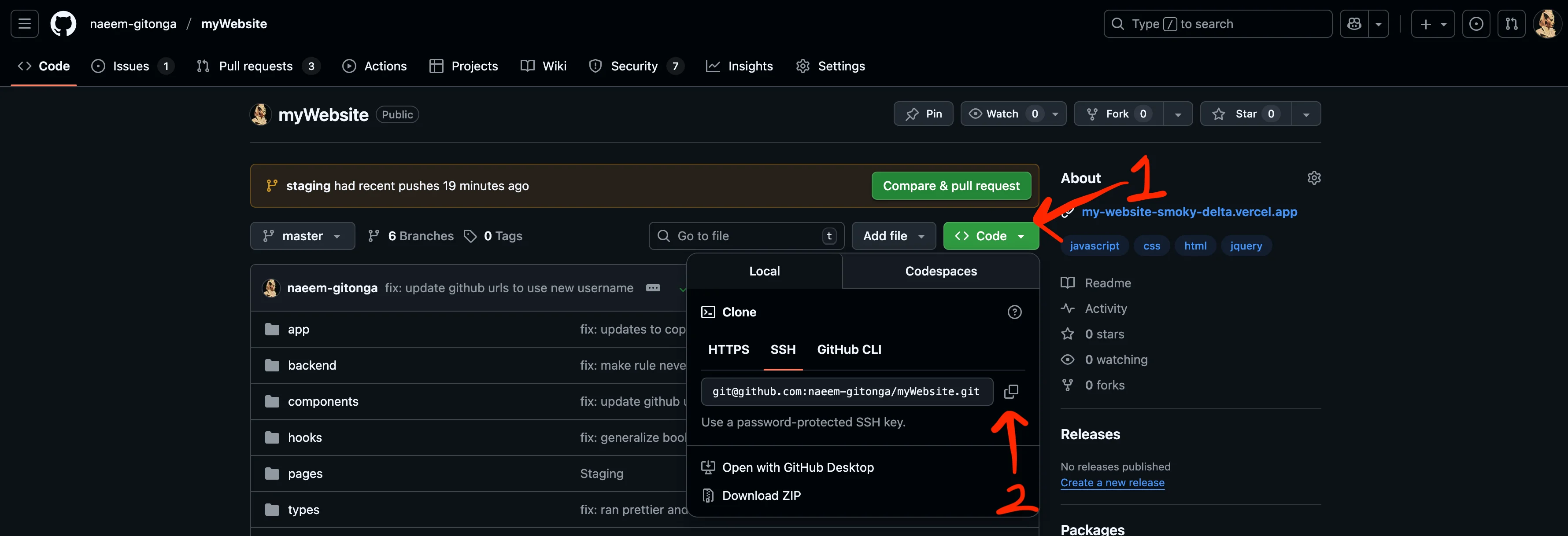
The URL that you copy will look like this:
git@github.com:naeem-gitonga/myWebsite.gitWe need to turn it into this:
ssh://git@github.com/naeem-gitonga/myWebsite.gitCopy the above. We'll use it in the next step.
Next, in Gitlab, go to Settings → Mirroring repositories
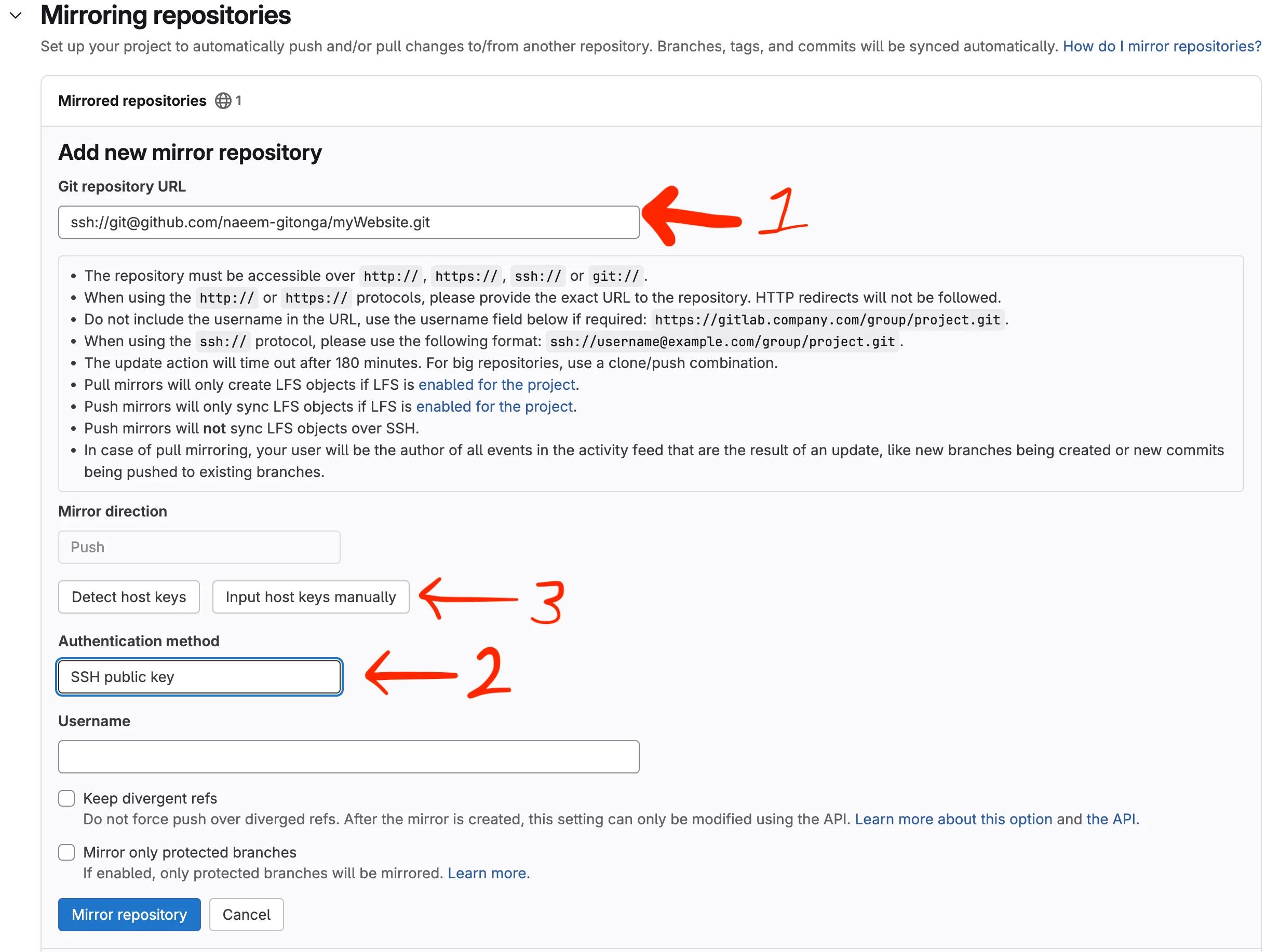
Next, update the repo SSH remote URL with the modified URL that we have above.
Then, make sure that you correct the Authentication Method. We need to use SSH Public Key. Choose that in the dropdown.
I prefer to input the host keys manually. This may or may not be the case for you. Press the Input host keys manually button. The following textarea will appear.
Next, run the following command from your terminal:
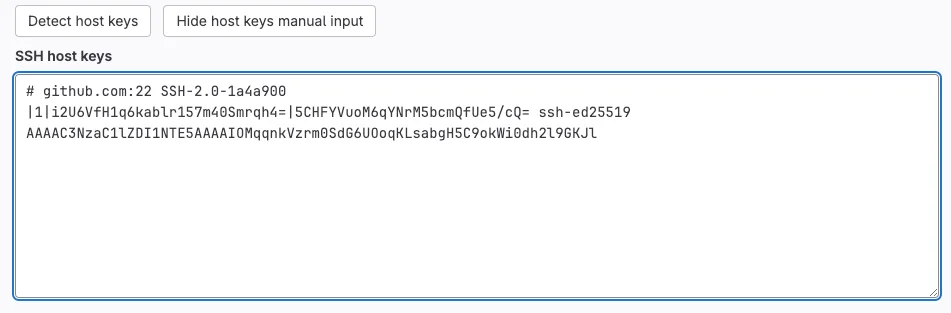
$ ssh-keyscan -H -t ed25519 github.comThen, copy the output and paste it in the SSH host keys textarea.
# github.com:22 SSH-2.0-1a4a900
|1|i2U6VfH1q6kablr157m40Smrqh4=|5CHFYVuoM6qYNrM5bcmQfUe5/cQ= ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIOMqqnkVzrm0SdG6UOoqKLsabgH5C9okWi0dh2l9GKJlIt should look like the following.
For me, I don't enter a username, nor do I check Keep divergent refs or Mirror only protected branches. The second option may be good to check if you have many feature branches and only want to capture changes that hit the important or protected branches.
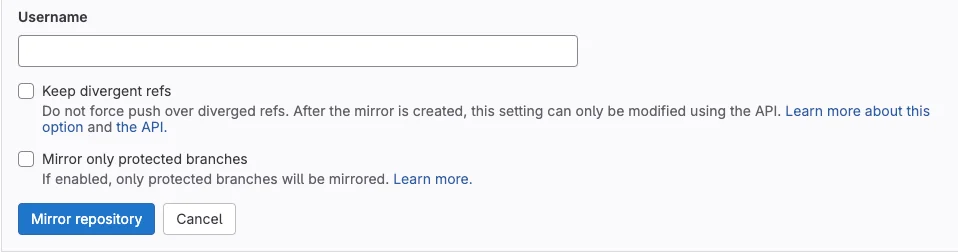
Again, this is a small project. I have two working branches so I am fine with neither of the two options checked.
Now, click Mirror Repository.
After you've clicked Mirror Repository, the box will collapse and you will be left with the following:
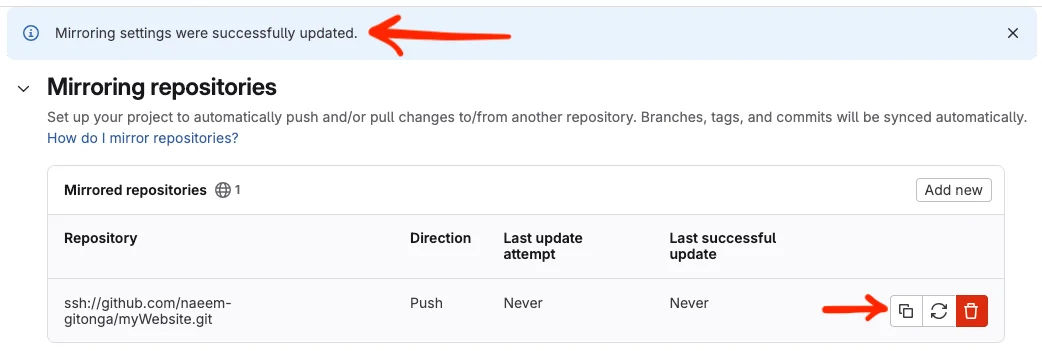
Now, the blue bar at the top is telling you that you have successfully created what you need on the Gitlab side.
Next, you'll need to click the copy button and head back over to Github. What you've just done was copy the Public Key for the SSH key pair that you created. Gitlab is managing the keys so you will not see the private key.
Almost done...
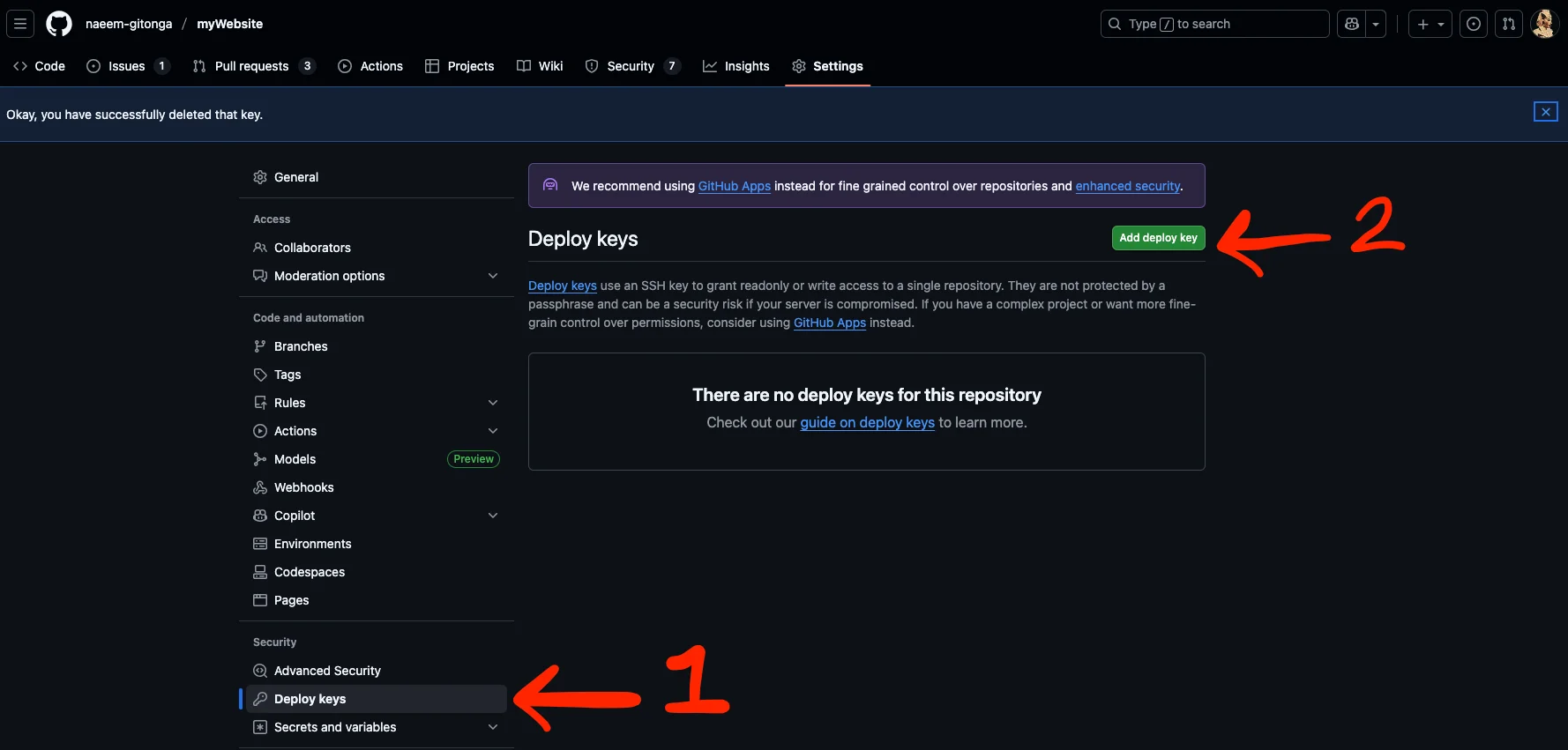
Now that the public key is on your clipboard, head back over to Github. In you're repo, go to Settings.
Then, click on Deploy keys and Add deploy key.
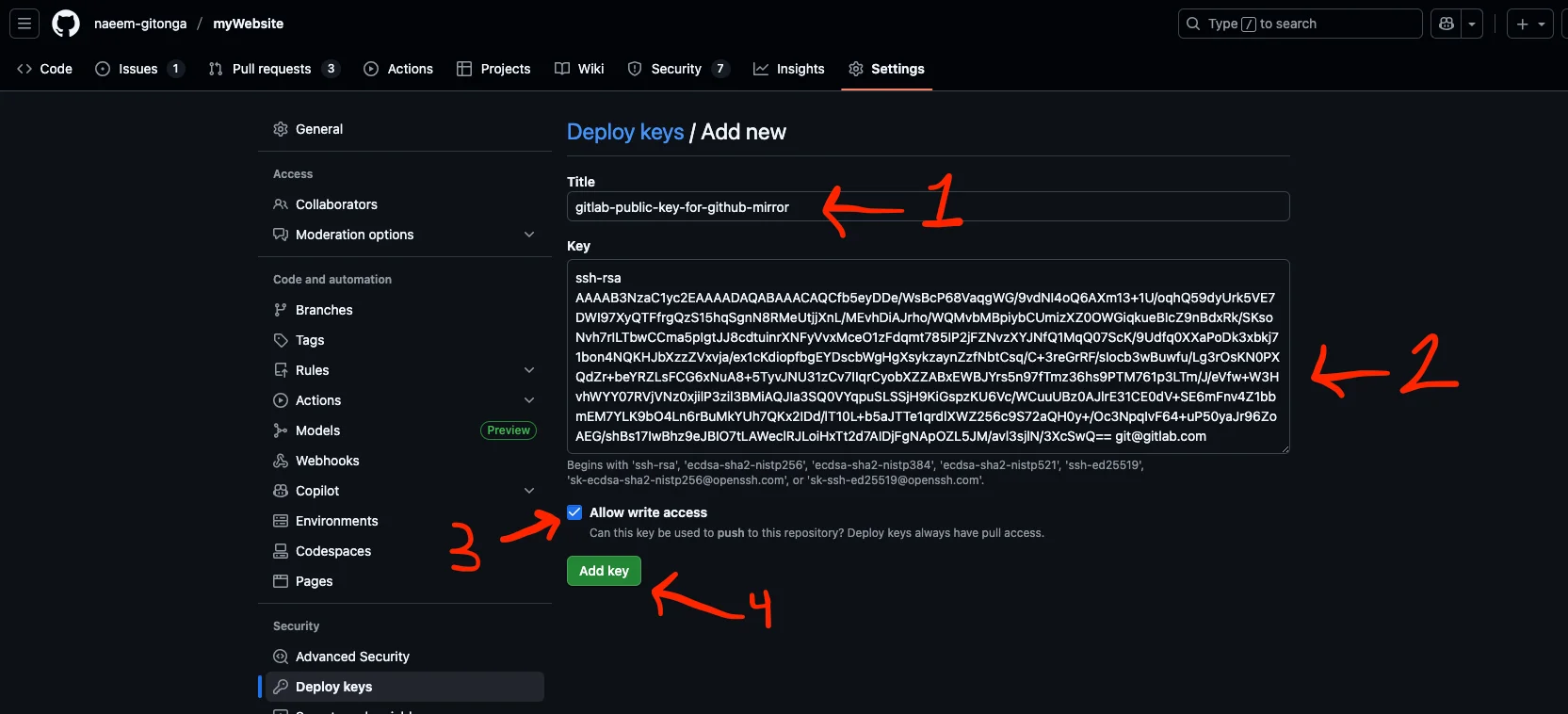
Once you've done that, you'll be able to give your new public key a title and add the key as depicted below. Make sure to check the box that says Allow write access. This will allow Gitlab to write to your Github repo. Click Add key to add the key and head back over to Gitlab.
Finally, you've added the key, all you need to do now is click the replay button shown below. This will start your mirror process.
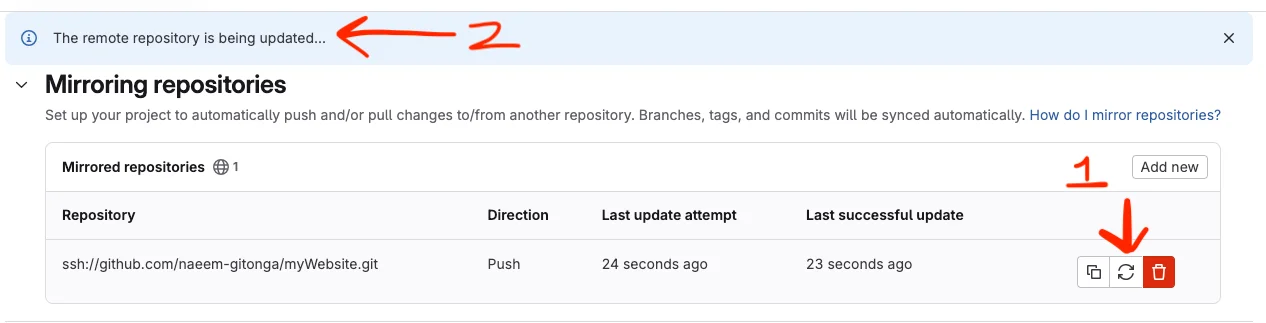
It may take a few minutes to make the initial push but you will see a blue banner telling you that the remote repository is being updated.
You did it!
When it finally does succeed you will see, back on the Github side, that your key has been used. And you should see your code now on Github. And that's it!
Errors?
If you have errors they certaintly have something to do with the SSH remote URL or how you have configured the authentication.
The official docs on Gitlab mirroring can be found here.
Github deploy key docs can be found here.
Thanks for reading!